Product overview:
Co-developed with Cytodiagnostics.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF or VEGF-A), also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a 45 kDa homodimeric, disulfide-linked glycoprotein produced by many cell types that facilitates angiogenesis and vasculogenesis.
The VEGF family includes VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, VEGF-E (Orf-VEGF), and PIGF (placental growth factor). There are multiple isoforms of VEGF-A expressed from alternative splicing of mRNA from a single VEGFA gene, among which VEGF165 is the most abundant isoform and essential for angiogenesis.
VEGF regulates a variety of functions, including proliferation and survival of endothelial cells, vascular permeability, cell migration in macrophage lineage, wound healing, bone formation, and development of embryonic vasculature. VEGF-A activates two receptors, VEGFR-1, and VEGFR-2, to regulate angiogenesis and vascular permeability, while VEGF-C and VEGF-D bind their receptor, VEGFR-3, mainly regulating lymphangiogenesis. VEGF expression is induced by hypoxia and cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha.
Our ELISA kit has several benefits:
- Ready to use. Simply add standards and samples directly to wells. No need for lengthy blocking or rehydration steps.
- High sensitivity, specificity and reproducibility.
- Fully validated in the sample types listed below.
- 96-well plate is breakable into 12 x 8 well strips.
Product Specification
|
Protein name |
VEGF |
|
Alternate names |
Vascular endothelial growth factor A, vascular endothelial growth factor A121, vascular endothelial growth factor A165, Vascular permeability factor, VEGF-A, VPF |
|
Species reactivity |
Human |
|
Assay format |
Solid-phase Sandwich ELISA (quantitative) |
|
Sample type |
Serum, Cell culture supernatant |
|
Sample volume |
100 μL |
|
Assay length |
4.5 hrs |
|
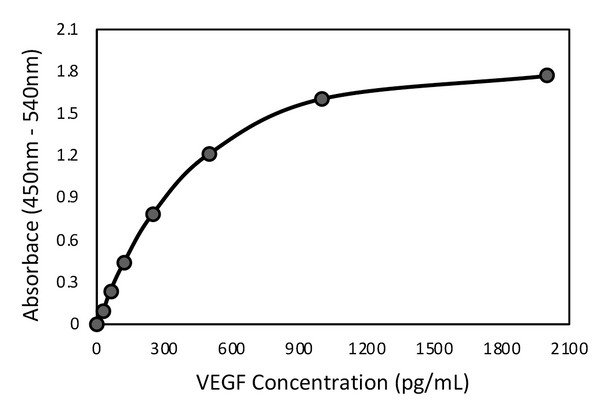
Analytical sensitivity |
<30 pg/mL |
|
Assay range |
31.25 – 2000 pg/mL |
|
Intra-assay CV |
<8% |
|
Inter-assay CV |
<10% |
|
Serum recovery |
95.3% |
|
Detection & Instrument |
Colorimetric, Microplate Reader |
|
UniProt ID |
(Human) P15692 |